Data Management
File Systems
There are several distinct file spaces available on clusters, each serving a different function.
- /ihome ($HOME), the system housing home directories.
- It contains sub-directories for each user group, and those contain individual user directories.
- Also referred to as the 'login directory' and is the entry point when a user logs into the CRC ecosystem
- 75 GB quota that cannot be increased
- /ix and /ix1, enterprise storage locations for persistent file storage.
- 5 TB provisions for new allocations can be found here.
- There is no charge for a 5 TB provision on ix.
- If you do not have a location provisioned, please let us know with this form.
- 5 TB increments of extra storage are available for purchase at a subsidized rate of $65 per TB per year.
- /bgfs, a BeeGFS file system for persistent file storage that is no longer being provisioned on.
- /zfs1 and /zfs2, 1 PB file systems for archival storage.
You can check your usage and quotas across these filesystems with the wrapper script crc-quota:
[nlc60@login0b ~] : crc-quota User: 'nlc60' -> ihome: 59.63 GB / 75.0 GB Group: 'sam' -> zfs1: 1.76 TB / 5.0 TB -> beegfs: 14.68 TB / 80.0 TB
File permissions
Group shared folders on /ix, /bgfs, /zfs1, or /zfs2 can be requested via ticket. The top level folder is owned by root:groupname with 2770 permission. The 2 sets the sticky bit, group members have read + write permission, and other users cannot access the folder.
- Access to files by the group members is governed by Unix file permissions. For detailed information on Unix file protections, see the man page for the chmod command.
- To share files with your group, give the group read and execute access for each directory from your top-level directory down to the directory that contains the files you want to share.
- chmod g+rx directory-name
- Then give the group read and execute access to each file you want to share.
- chmod g+rx filename
- To give the group the ability to edit or change a file, add write access to the group:
- chmod g+rwx filename
- If you want to share file with other group members or users, submit a help ticket and we can use Access Control Lists (ACLs) – a more fine-grained control than Unix file permissions allow. The command for bgfs is setfacl, and for ZFS is nfs4_setfacl. There are man pages for chmod, setfacl and nfs4_setfacl.
Shared Folders
iX storage locations are only accessible to allocation owners and the users they sponsor (their "user group").
If you are working with collaborators that also have CRC user accounts, but are not in your user group, a shared folder under your iX location can be used to facillitate sharing data between your groups.
These should be requested by submitting a ticket and providing details about the users that need access.
This should include Pitt Usernames and specifics about the permssions they will require (read, write, execute, etc).
Restoring Accidentally Deleted Files
Both ixSystems and ZFS keep snapshots for up to 7 days.
Submit a help ticket with your request to restore data from snapshots.
Snapshots are not available for BGFS.
Moving Data between your local machine and the CRC Clusters
SFTP Clients
CyberDuck
CyberDuck is a popular open source SFTP client for Windows and Mac. Download and install Cyberduck. Open the Cyberduck application. Click the "Open Connection" button on the toolbar.
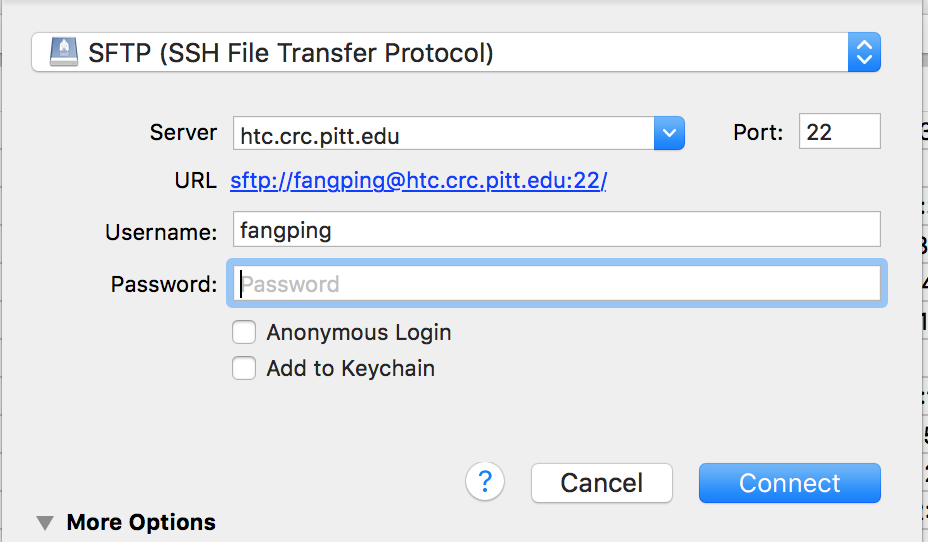
- Select "SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol)" from the drop-down.
- Enter htc.crc.pitt.edu in the Server box.
- Enter your Pitt username and password, and click Connect.
Your files on the server will appear in the CyberDuck window. You can now drag-and-drop files to and from the window to upload/download files.
FileZilla
FileZilla is cross-platform FTP application available for Windows, Linux, and macOS. Download and install FileZilla. Open the FileZilla application.
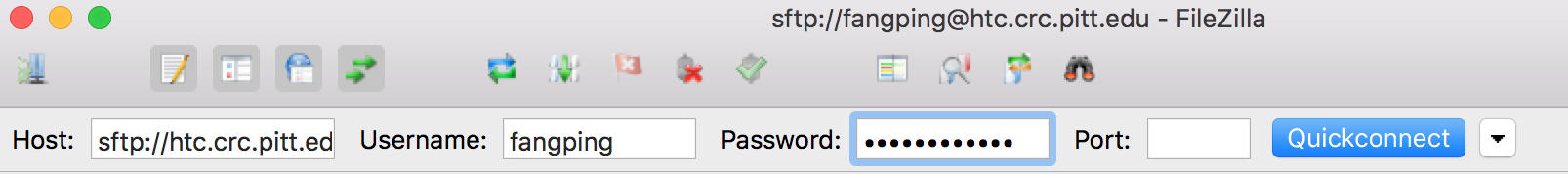
- Enter sftp://htc.crc.pitt.edu in the Host box.
- Enter your Pitt username and password, and click QuickConnect.
Your files on the server will appear in the FileZilla window.
Web Tools
Ondemand File App
Logon ondemand.htc.crc.pitt.edu, Click Files -> Home Directory, Click Upload and choose File(s) from your computer. Due to limited cache size, DO NOT use Ondemand File App to upload big files ( > 1 GB).

Globus
For large data sets, consider using Globus.
An institutional endpoint is not required to use Globus; You can set up a personal endpoint on your computer if you need to transfer large amounts of data.
Command Line Tools
rsync
From a terminal/shell on your computer, you will issue your rsync command.
rsync -aP files fangping@htc.crc.pitt.edu:/bgfs/sam/fangping/
This makes a recursive copy of local directory files on the computer you issued the command on to a folder on the cluster. -P is --partial --progress.
rsync -aP fangping@htc.crc.pitt.edu:/bgfs/sam/fangping/files/ .
This copies the /bgfs/sam/fangping/files folder on the cluster to the current directory on the computer you issued the command.
scp
From a terminal/shell on your computer, you will issue your SCP command.
scp -r files fangping@htc.crc.pitt.edu:/bgfs/sam/fangping/
This copies the folder files in the current directory on the computer you issued the command on to a folder on the cluster.
scp -r fangping@htc.crc.pitt.edu:/bgfs/sam/fangping/files/ .
This copies the /bgfs/sam/fangping/files folder on the cluster to the current directory on the computer you issued the command.
aspera
Aspera is IBM's high-performance file transfer software which allows for the transfer large files and data sets with predictable, reliable and secure delivery regardless of file size or transfer distance from a location that has the aspera transfer server running. The NCBI recommend the use of aspera for transfer of data sets from their site.
Download aspera from to your home directory on HTC cluster.
Download link: https://download.asperasoft.com/download/sw/connect/3.9.1/ibm-aspera-con...
tar xzvf ibm-aspera-connect-3.9.1.171801-linux-g2.12-64.tar.gz
You will find file ibm-aspera-connect-3.9.1.171801-linux-g2.12-64.sh
./ibm-aspera-connect-3.9.1.171801-linux-g2.12-64.sh
aspera is installed to ~/.aspera
You can then use aspera to download files. aspera binary is at ~/.aspera/connect/bin/ascp and the key is at ~/.aspera/connect/etc/asperaweb_id_dsa.openssh
[fangping@login0b aspera]$ ~/.aspera/connect/bin/ascp -QT -l 300m -P33001 -i ~/.aspera/connect/etc/asperaweb_id_dsa.openssh era-fasp@fasp.sra.ebi.ac.uk:/vol1/fastq/SRR949/SRR949627/SRR949627_1.fastq.gz .
Cloud Resources
Pitt OneDrive
You can transfer data between Pitt OneDrive and the cluster. Follow these steps.
Pitt Box
You can transfer data from and to Pitt box from the cluster. Follow these steps.
AWS S3
awscli has been installed as a module. You can transfer data from the cluster to AWS S3.
module load awscli/1.16.135
aws s3 sync /bgfs/sam/fangping/DataUpload s3://my-s3-bucket/data_from_htc
This will transfer /bgfs/sam/fangping/DataUpload folder to s3://my-s3-bucket/data_from_htc
You can submit this command as a job on HTC computational node.
google bucket
You can install and configure gsutil to transfer data from/to gs bucket.
module load gsutil/5.16
gsutil config
gsutil cp -r gs://gs-bucket-name/ .
This will recursively transfer gs://gs-bucket-name/ folder to the current folder.
Azure Storage
AzCopy is a command-line tool that moves data into and out of Azure Storage. azcopy has been installed as a module.
module load azcopy/10.11.0
azcopy --help
azcopy copy "/bgfs/your/folder/" "https://account.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer1/?sv=2018-03-28&ss=bjq..." --recursive=true
This example command recursively copies data from a local directory to a blob container. A fictitious SAS token is appended to the end of the container URL.
You can submit this command as a job on HTC computational node.
